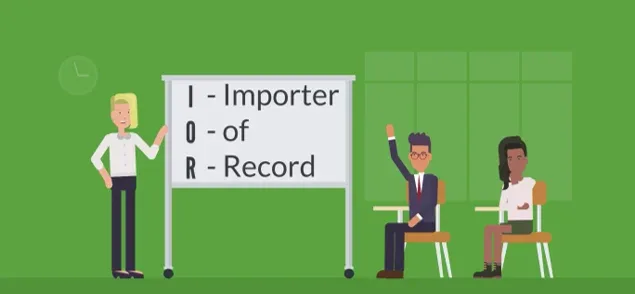
Importer Of Record Definition
The Importer of Record is the foundation for any successful international trade transaction. Knowing who handles import taxes, duties, and compliance regulations is essential. It is vital to determine how to conduct business in a foreign market.
Effective use of an Importer of Record service can also reduce costs. It optimizes the customs clearance process and avoids delays in product delivery. Besides, it protects companies from costly penalties resulting from incorrect or incomplete documentation.
Furthermore, understanding the implications of having an IOR service provider is essential. It creates a long-term strategy and builds relationships with local suppliers and customers.
IOR Process
Managing the IOR (Installation, Operation, and Maintenance) process effectively involves several key steps and considerations to ensure smooth execution and optimal performance of the systems or equipment involved. Here’s a structured approach to manage the IOR process:
1. Preparation Phase:
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline the goals and expected outcomes of the IOR process. This could include functionality requirements, performance metrics, and compliance with standards.
- Allocate Resources: Determine the resources required for installation, operation, and ongoing maintenance. This includes personnel, equipment, tools, and budget.
- Create a Timeline: Develop a timeline that includes milestones for installation, testing, commissioning, and regular maintenance tasks.
2. Installation Phase:
- Detailed Planning: Create a detailed installation plan that covers tasks, responsibilities, safety measures, and contingency plans.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure installation procedures adhere to manufacturer guidelines, industry standards, and regulatory requirements.
- Testing and Verification: Thoroughly test and verify installed equipment or systems to ensure proper functionality and alignment with specifications.
3. Operation Phase:
- Training: Train operators and maintenance personnel on how to operate the equipment/system correctly and safely.
- Monitoring and Control: Implement systems for real-time monitoring and control of the equipment to ensure it operates within specified parameters.
- Documentation: Maintain accurate documentation of operation procedures, maintenance schedules, and any modifications made to the system.
4. Maintenance Phase:
- Scheduled Maintenance: Establish a regular maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and operational requirements.
- Predictive Maintenance: Use predictive maintenance techniques, such as condition monitoring and data analytics, to anticipate and prevent equipment failures.
- Emergency Response: Develop protocols for responding to emergencies or unexpected failures to minimize downtime and mitigate risks.
5. Continuous Improvement:
- Feedback Mechanism: Establish a feedback mechanism to gather input from operators, maintenance personnel, and users to identify areas for improvement.
- Performance Review: Review performance metrics regularly to assess the efficiency, reliability, and safety of the equipment/system.
- Upgrades and Enhancements: Implement upgrades or enhancements based on technological advancements or changing operational requirements.
6. Compliance and Safety:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that all aspects of the IOR process comply with relevant regulations, codes, and standards.
- Safety Procedures: Prioritize safety throughout the IOR process by conducting risk assessments, implementing safety protocols, and providing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
7. Communication and Coordination:
- Stakeholder Engagement: Throughout the IOR process, maintain open communication with stakeholders, including project managers, suppliers, contractors, and end-users.
- Coordination: Coordinate activities between different teams (installation, operations, maintenance) to ensure smooth transitions and minimize disruptions.
8. Documentation and Reporting:
- Record Keeping: Maintain comprehensive records of all installation, operation, and maintenance activities for future reference and auditing purposes.
- Reporting: Generate regular reports on the status of the equipment/system, including performance metrics, maintenance activities, and any issues encountered.
Challenges of Importing and International Trade
One of the biggest challenges for importers is the complex regulations associated with international trade. Importers must understand many laws related to each country. Rules and regulations and duties, taxes, or tariffs differ between countries. Additionally, many countries have specific requirements for the goods they accept. Including labeling, packaging, or documentation that certain imports must provide. Not only does this need much research and knowledge to ensure compliance, but it can also lead to costly delays if not done correctly.
Another challenge importers face ensuring product quality control when shipping from another country. Quality assurance processes. They can be challenging to put in place when dealing with overseas suppliers. Since they are often located in different time zones, language barriers may exist. As such, importers must work very closely with their suppliers. To ensure quality standards are consistently met, and products delivered meet customer expectations. Finally, currency fluctuations make it difficult for an importer to determine accurate activities. Including a budget, plan expenses, and forecast sales. They also determine the price of goods shipped internationally due to changing exchange rates.
Benefits of Using an Importer of Record
An Importer of Record (IOR) handles fulfilling import paperwork and regulations. Besides payment of taxes and duties on goods entering a country. Utilizing an IOR can provide considerable benefits to businesses looking to expand globally.
First, an IOR ensures compliance with international trade laws while reducing associated risks. They know their respective area’s required customs rules and procedures. They enable companies to enter the global market without worrying about potential fines. As IOR service providers, make sure not to have any incorrect paperwork or other issues. An experienced IOR also helps decrease costly delays in shipment arrivals. Since they resolve on-the-spot customs clearance issues that may arise during the process.
Furthermore, having an IOR allows businesses to avoid extra costs. In particular, the coasts while importing goods from abroad into their local market. Due to the IOR service provider’s understanding of local taxes and tariffs.
Compliance Considerations for a Successful IOR Service Provider
One of the most critical aspects of international trade is compliance. Importers and exporters must understand their legal obligations. Plus, remaining compliant with the laws, regulations, and policies set by countries worldwide. IOR international providers must consider compliance when importing goods from another country.
The first step for any company engaging in international trade is to identify an IOR. IORs responsibilities are ensuring that all applicable laws are met. They also can face considerable fines or penalties if found in violation. As such, it is vital to ensure that all paperwork related to the import process is completed correctly and accurately. This includes obtaining any necessary licensing or permits and submitting customs declarations. Plus keeping records of transactions paying duties and taxes on time.
Besides understanding local laws, companies should become familiar with global standards. Including those established by the World Customs Organization (WCO) or the United Nations. And Convention on Contracts for International Carriage of Goods Wholly or Partly by Sea (UNCITRAL). These standards help ensure consistent compliance across different countries. At the same time, mitigating risks associated with cross-border trade activities.
When selecting an importer of record, companies should consider many aspects. Including cost, compliance expertise, customer service support, and reliability factors. Companies should also ensure that they work with a compliant Importer of Record( IOR) service. He must understand the laws in their origin country and destination market.
Learn more about IOR
FAQs
What does it mean to be an importer of record?
As the Importer of Record (IOR), I am formally recognized by various governments as the individual or entity owning or buying imported products in a destination country. I can be the owner, buyer, or authorized customs broker.
Who is the exporter and importer of record?
As the Importer of Record (IOR), I’m the one in charge of handling all the payments for duties, tariffs, and fees associated with the imported goods. Think of me as the representative for the importer. Now, let’s talk about the Exporter of Record (EOR): It deals with the same aspects as the IOR, but it comes into play for export operations instead of imports.
Is the importer of record the buyer?
As per Customs and Border Protection (CBP), being the Importer of Record means I’m the one responsible for making sure we follow all the rules when bringing goods in. Whether I’m the one sending, receiving, or a third party, the designation as IOR is usually decided by the shipment’s Incoterms.
How do you determine the importer of record?
The Importer of Record is the person or entity who owns, purchases, or receives the goods when they are imported. Interestingly, a licensed Customs broker, given the authority by the owner, purchaser, or consignee, can also take on the role of the IOR. So, the Importer of Record could be a person or a business.
How long must the importer keep these import records?
Store all pertinent commercial documents and transaction records at the depot for a minimum of five years, unless authorized by the ABF to keep them elsewhere.

Recent Comments